Are you aware that there are currently over 61,000 live websites using Angular, and nearly 900,000 more that have used it historically?
Yes, Angular is still a go-to framework for scalable, high-performance web apps. Companies like Google (Gmail, Google Ads), PayPal, JetBlue, and Netflix rely on it to power serious production workloads.
But what happens when content rendered on the client side goes unseen by search engine crawlers? Well, visibility suffers, and so does growth.
In a digital ecosystem where:
- 53% of web traffic originates from organic search
- Angular was used by 20.39% of developers in 2023
- SEO delivers a 5x ROI over paid search
… failing to optimize Angular for SEO is a missed opportunity.
Next, we’ll show you how to make your Angular app show up in search; clean, fast, indexable, and built to win traffic without relying on ads.
Let’s begin.
TL;DR
- Angular apps don’t rank by default; search engines struggle with client-side rendering.
- Server-side rendering (SSR) and prerendering are your SEO foundation.
- Meta tags, structured data, and routing need custom handling in Angular.
- Performance matters: Core Web Vitals and load speed directly impact rankings.
- Angular Universal, Scully, and AI coding tools help teams ship SEO fixes faster.
- Skip these steps, and your site stays fast but invisible.
What Angular SEO Means in 2026
Angular is a component-based web framework built and maintained by Google. It’s known for its performance, code structure, and ability to power dynamic single-page applications (SPAs).
But when it comes to SEO, Angular apps don’t follow the same rules as traditional websites.
So, Angular SEO refers to the set of strategies and technical fixes that make Angular applications easier to crawl, index, and rank in search engines.
Why Angular Is Not SEO-Friendly by Default
Angular apps rely on client-side rendering. That means most of the page content doesn’t exist in the initial HTML; it gets loaded dynamically in the browser using JavaScript.
For users, this works. But, for search engines, it creates friction.
Googlebot and other crawlers expect content to be present in the source code. If it’s not there, indexing becomes unreliable or delayed. Your page might appear blank to crawlers. Or worse, get skipped entirely.
Unless you take extra steps, search engines won’t see what your users see.
Angular vs Traditional Server-Rendered Sites
Server-rendered sites generate full HTML content on the backend before sending it to the browser. Crawlers can access everything immediately, with no extra processing.
Angular doesn’t do this by default. You have to enable server-side rendering or prerendering manually.
Without it, your app sends a shell of a page: scripts, skeletons, and very little actual content.
Why SEO Still Matters for Angular Applications
Despite what many devs assume, Angular doesn’t make your content visible by default.
You need SEO built into the architecture. And with Angular’s continued market presence, ignoring that reality means falling behind.
The numbers say it all:
- Angular powers over 360,000 websites globally.
- 17.1% of developers actively choose it for serious production work.
- In 2024 alone, it was downloaded more than 392,000 times.
That scale comes with competition. If you’re not optimizing for visibility, someone else is.
Here’s what strong SEO does for Angular apps:
- Increases traffic: As noted earlier, organic search accounts for 53% of all website traffic. So, you either show up there, or you don’t exist.
- Improves credibility: Higher-ranking pages earn more trust. When your Angular app ranks well, users assume your product is more legit.
- Maximizes content reach: With proper SSR or prerendering, Angular content becomes fully indexable, giving it a clear path to visibility in search.
- Sustains traffic and lead flow: SEO brings in consistent traffic without the cost of ads. Once it’s set up right, it keeps working in the background day after day.
- Puts you ahead of less optimized competitors: Most Angular apps aren’t built with SEO in mind. If yours is, you’re instantly better positioned to rank.
Skipping SEO doesn’t just hurt visibility; it undermines the performance of the entire app.
Core SEO Challenges in Angular Apps
Angular is a powerful framework for building interactive web apps. But it doesn’t play nice with search engines by default.
Without the right technical setup, Angular apps tend to hide content from crawlers. They also delay meaningful page rendering and introduce friction in everything from metadata to URL structure.
Here are the biggest SEO blockers developers face when working with Angular:
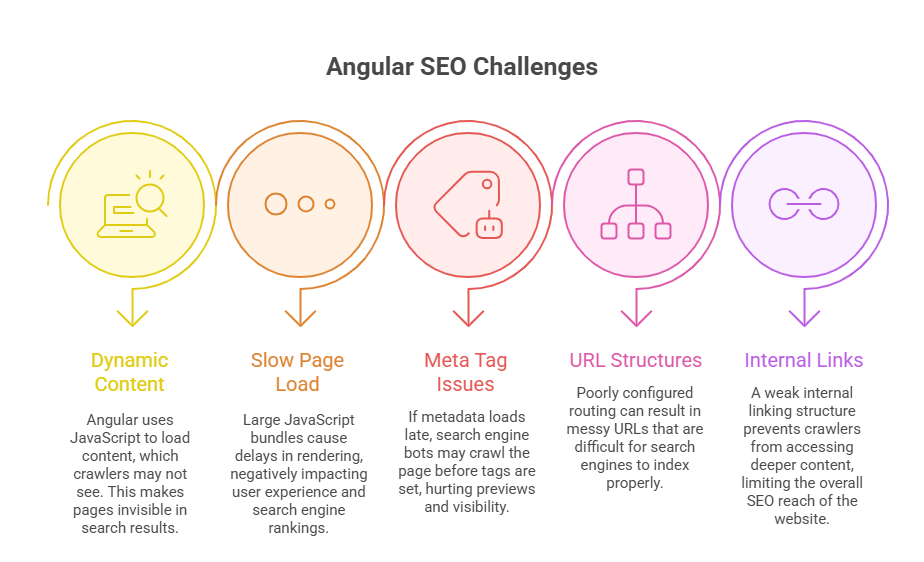
1. Dynamic Content Rendering
Angular apps render content in the browser using JavaScript. That’s fine for users, but it’s a problem for bots that crawl static HTML.
If the content isn’t present in the initial source code, search engines may fail to index it. And if they can’t index it, it won’t rank, no matter how good the UX is.
2. Slow Initial Page Load
Apps built with the popular Angular framework tend to ship large JavaScript bundles. That slows down first paint and delays content visibility, especially on mobile or slower connections.
Page speed is a known ranking factor. If your site loads slowly, it’s not just UX that takes a hit; your search performance drops with it.
3. Incomplete Meta Tag Management
Angular doesn’t handle metadata like title tags, descriptions, Open Graph, or X (formerly Twitter) Cards out of the box. These are typically set on the client side.
That creates a timing issue: crawlers may hit the page before meta tags are loaded, resulting in missing or incorrect metadata in search results.
4. Complicated URL Structures
Angular’s routing system can produce URLs that are harder to manage from an SEO standpoint. Especially when client-side routing is misconfigured.
Clean, crawlable URLs matter. But in Angular, they require extra care to avoid hash fragments, parameter bloat, or broken canonical logic.
5. Limited Crawlability of Internal Links
Without proper markup and routing configuration, internal links in Angular apps can become invisible to crawlers.
That limits how deeply search engines can index your content. Poor internal linking means fewer pages get crawled, and fewer chances to rank.
Top Angular SEO Best Practices
SEO in Angular takes a different toolkit than in traditional setups.
You’re not just setting meta tags and walking away; every core SEO element requires a technical decision.
Here’s how to do it right:
1. Implement Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Server-side rendering gives Angular apps a major edge in SEO. Instead of waiting for JavaScript to render content on the client side, the server sends fully rendered HTML to the browser and to search engine crawlers.
Angular Universal supports SSR, improving SEO and load time by up to 50%. This is especially useful for content-heavy websites, where visibility and speed go hand in hand.
Some benefits of SSR include:
- Faster initial load time
- Better indexing by search engines
- Cleaner previews when shared on social platforms (thanks to preloaded OG tags)
Pro Tip: A best practice you can apply is to cache your rendered pages to keep load times fast and consistent.
2. Use Prerendering for Static Pages
For sites with many static or semi-static pages, prerendering can reduce server load and improve performance.
It generates static HTML at build time, ideal for pages that don’t change often.
Recommended tools:
- Prerender.io
- Scully (static site generator for Angular)
3. Optimize Dynamic Meta Tags
Search engines rely heavily on metadata to understand and rank pages. Angular apps require you to generate these dynamically, route by route.
Each page should have its own set of metadata:
- Title
- Meta description
- Canonical tag
- OG tags
- Twitter cards
Angular’s Meta and Title services help you inject and update these programmatically. If you skip this step, you risk blank previews, duplicate snippets, or incorrect indexing.
4. Improve Angular Routing and Canonical Structure
Angular routing isn’t SEO-ready by default. Misconfigured routes can confuse bots, trigger crawl errors, or produce inconsistent URLs.
To stay clean:
- Avoid using /#/ in URLs
- Make sure your server handles Angular routes correctly (e.g., fallback to index.html)
- Define clear canonical tags to avoid duplicate content
Fixing routing issues early prevents bigger indexing problems down the line.
5. Create an XML Sitemap and Robots.txt
You can’t rank what Google can’t find.
A clean XML sitemap tells crawlers where your content lives. Your robots.txt file defines what they can or can’t access.
Best practices include:
- Auto-generate a sitemap and update it regularly
- Submit it via Google Search Console
- Check that robots.txt isn’t blocking critical routes or assets
This makes crawling smoother, especially in large apps.
6. Ensure Fast Load Times and Core Web Vitals Compliance
Angular’s performance has a direct impact on rankings. If your app is slow to load or sluggish on mobile, Google notices and penalizes.
Tighten up your delivery with:
- Lazy-loaded modules
- Ahead-of-Time (AOT) compilation
- Compressed JavaScript bundles
- Gzip or Brotli compression
- Minified CSS and JS
- Optimized images and assets
Use Google Lighthouse or PageSpeed Insights to identify bottlenecks and benchmark improvements.
7. Structured Data Markup (Schema.org)
Structured data improves how your pages appear in search; think star ratings, product info, article details, etc.
Angular doesn’t auto-generate this. You’ll need to insert JSON-LD manually in your templates.
Good starting points:
- Use Article schema for blog posts
- Use Product schema for ecommerce items
Rich results start with a solid schema.
8. Mobile-First Optimisation
Mobile usability is a ranking factor. If your Angular app breaks on smaller screens, you’re losing visibility and conversions.
Make sure your site:
- Uses responsive layouts
- Has buttons and tap targets that work well on touchscreens
- Loads fast on 4G or slower connections
- Doesn’t hit users with pop-ups or interstitials
Mobile-first is expected, not optional
9. Monitor SEO and Performance Metrics
You can’t improve what you don’t measure. Track both technical SEO and content performance using:
- Google Analytics
- Google Search Console
- Bing Webmaster Tools
Also, set clear benchmarks (like bounce rate, crawl errors, or average position) and monitor them weekly. The earlier you catch SEO issues, the less they’ll cost you.
Common Angular SEO Mistakes to Avoid
Some mistakes can seriously hurt your Angular app’s SEO performance. Here are the ones to watch out for:
Ignoring Server-Side Rendering (SSR)
Relying entirely on client-side rendering creates SEO problems.
So, use Angular Universal with prerendering to serve fully rendered HTML when search engines request content. This ensures that crawlers receive everything they need up front.
Overlooking Meta Tags and Titles
Failing to optimize meta titles and descriptions weakens your presence in search results.
It’s critical to configure Angular’s Meta and Title services correctly on a per-page basis. Skipping this step leads to poor previews and missed keyword opportunities.
Poor URL Management
Hash-based URLs don’t play well with crawlers.
Use Angular’s PathLocationStrategy to implement clean, crawlable URLs. This avoids fragment identifiers (/#/) and supports better indexation.
Skipping Lazy Loading
Loading all modules upfront slows down page load time, especially for large apps.
So, implement lazy loading to reduce initial payload and improve Core Web Vitals. Faster pages rank better and convert more consistently.
Not Handling 404 Pages Properly
Broken links damage SEO if they aren’t managed correctly.
Always set up a functional 404 page and return proper HTTP status codes for missing content. This helps preserve crawl integrity and avoids confusing bots.
Recommended Tools for Angular SEO
You don’t have to do it all manually, especially not in 2026.
AI-powered code assistants now boost developer productivity by up to 30%, according to McKinsey. That means less time wrestling with config files and more time getting your SEO stack in place.
Here are the tools that actually make Angular SEO easier to handle, from rendering to performance to crawling:
- Angular Universal (SSR)
- Scully (Static site generation)
- Prerender.io (Prerendering service)
- Google Search Console (Monitoring)
- PageSpeed Insights (Performance analysis)
- Lighthouse (Technical SEO audits)
- Ahrefs/Semrush (Advanced SEO insights)
Bottom Line: Turn Angular Into an SEO-Ready Machine
Angular doesn’t have to be an SEO black box.
Yes, it takes extra setup. And no, it’s not plug-and-play like traditional frameworks. But when you follow the right practices, you give your app a real shot at visibility.
Google won’t wait for your scripts to load. Neither should your users.
So, get the technical foundation right, and track performance like it matters (because it does). That way, you’ll stop building apps that no one sees.
FAQs
What is Angular SEO, and why is it important for web developers?
Because Google doesn’t wait for your app to render. Angular SEO is about making sure your content actually shows up for crawlers. That means server-side rendering, clean routing, and metadata that loads when it matters, not three seconds later.
Is Angular good for SEO?
It can be. Not by default, though. Angular needs extra steps to be search-friendly. But once you set it up right, it performs just as well as any other framework.
Is Angular still used in 2026?
Yes, and not just in side projects. Angular is backed by Google and powers thousands of serious, production-grade apps. If you’re building at scale and need structure, Angular’s very much alive, and search engine optimization still matters.
How can I optimize Angular applications for better SEO performance?
Start with SSR or prerendering. Then fix your metadata, clean up your URLs, add structured data, speed up your load times, and test everything. You don’t need magic, just the right stack and a checklist you actually follow.
What are the common challenges of SEO in Angular applications, and how to overcome them?
The biggest offenders: content that never shows up in source, slow initial loads, bad metadata timing, messy internal links, and weird URLs. The fix? Angular Universal, smart routing, dynamic meta services, and tools that catch issues before Google does.